Car accidents place intense force on the spine, often leading to back pain, stiffness, or serious injury. Damage may involve muscles, ligaments, discs, or the spinal cord. Early evaluation helps prevent long-term problems and supports safer recovery. Below are six of the most common back injuries after a crash, along with key signs to watch for.
1. Whiplash & Soft Tissue Injuries
Whiplash and other soft tissue injuries occur when sudden force stretches or tears the muscles, ligaments, and tendons in the neck or back. This often happens in rear-end or high-impact collisions and can lead to pain, stiffness, and limited movement.
Common symptoms may include:
- Neck or upper-back pain
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Headaches
- Shoulder or arm discomfort
- Muscle tenderness or spasms
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Evaluation may include a physical exam and imaging if needed to rule out serious injury. Treatment often involves rest, pain-relieving medication, physical therapy, ice or heat therapy, and gradual return to activity.
When to seek medical care:
Seek care if pain is severe, symptoms last longer than a few days, or you experience numbness, weakness, dizziness, or difficulty moving your neck. Early treatment helps reduce complications and supports recovery.
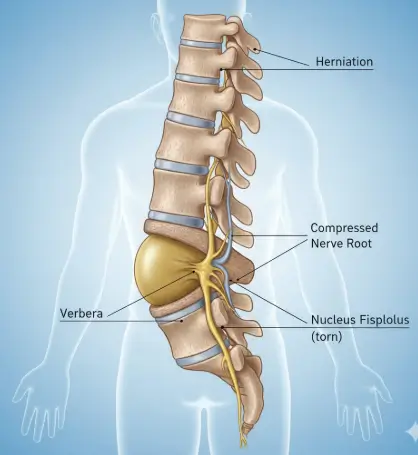
Herniated Discs (Slipped Discs)
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner core of a spinal disc pushes through a tear in its outer layer. This can irritate nearby nerves, leading to back or neck pain and symptoms that may travel into the arms or legs. Car accidents can cause sudden disc damage due to forceful impact.
Common symptoms may include:
- Sharp or radiating back or neck pain
- Pain traveling into the arms or legs (sciatica)
- Numbness or tingling
- Muscle weakness
- Pain that worsens with bending, lifting, or twisting
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis may include a physical exam and imaging such as MRI or CT scans to confirm disc damage. Treatment often begins with medications, physical therapy, activity modification, and sometimes injections. Surgery may be considered if severe nerve compression, weakness, or persistent pain occurs.
When to seek medical care:
Get medical evaluation if you experience severe pain, worsening numbness or tingling, weakness in arms or legs, difficulty walking, or pain that does not improve with rest or basic treatment. Early care helps protect nerve function and supports better recovery.
Spinal Fractures
Spinal fractures occur when one or more vertebrae crack or collapse, often from high-impact car accidents, falls, or severe trauma. These injuries can range from mild compression fractures to unstable breaks that threaten spinal cord and nerve health. Early evaluation is important to prevent long-term complications.
Common symptoms may include:
- Sudden, severe back pain
- Pain that worsens with movement, standing, or bending
- Limited mobility or stiffness
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness if nerves are affected
- In severe cases, loss of bladder or bowel control
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis typically includes a physical exam and imaging such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI to determine fracture type and severity. Treatment may involve bracing, pain management, physical therapy, or minimally invasive procedures like vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Severe or unstable fractures may require surgical stabilization.
When to seek medical care:
Seek immediate care after any serious accident or if you develop severe or worsening back pain, nerve symptoms, difficulty walking, or bowel/bladder changes. Prompt treatment helps restore stability, protect the spinal cord, and support safe recovery.
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI)
A spinal cord injury occurs when trauma damages the spinal cord or surrounding nerves. Car accidents are one of the most common causes. Injury can disrupt the brain’s ability to send signals to the body, potentially affecting movement, sensation, and body function below the level of injury.
Common symptoms may include:
- Severe back or neck pain
- Numbness, tingling, or loss of sensation
- Weakness or loss of movement in arms or legs
- Loss of coordination or balance
- Difficulty breathing, walking, or standing
- Changes in bowel or bladder control in severe cases
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Evaluation often includes a neurological exam and imaging such as X-ray, CT scan, or MRI. Treatment focuses on stabilizing the spine, reducing swelling, preventing further damage, and protecting nerve function. Care may include medications, bracing, surgery, and specialized rehabilitation to restore strength and function as much as possible.
When to seek medical care:
Seek emergency care immediately if a spinal cord injury is suspected after a car accident. Early treatment is critical to protect the spinal cord, reduce complications, and improve recovery outcomes.
Facet Joint Injuries
Facet joints are small joints located between the vertebrae that help guide and stabilize spinal movement. During a car accident, sudden impact or twisting force can irritate, inflame, or injure these joints. Damage may involve joint cartilage, surrounding ligaments, or the joint capsule, leading to localized back or neck pain.
Common symptoms may include:
- Localized pain in the neck, mid-back, or lower back
- Pain that worsens with bending, twisting, or extending the spine
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Muscle tightness or spasms near the injured area
- Pain that may radiate to the shoulders, buttocks, or thighs (but usually not below the knee)
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosis often involves a physical exam, imaging studies, and sometimes diagnostic injections to confirm the pain source. Treatment may include rest, medications, physical therapy, bracing, and targeted injections. In certain cases, radiofrequency ablation or minimally invasive procedures may help reduce chronic pain.
When to seek medical care:
See a doctor if back or neck pain persists, worsens over time, limits movement, or interferes with daily activities. Early evaluation helps relieve pain, prevent further joint irritation, and support safe recovery.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis occurs when the space within the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots. Car accidents can worsen existing narrowing or trigger inflammation that compresses nerves, causing pain and mobility problems.
Common symptoms may include:
- Back or neck pain
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the arms or legs
- Pain or cramping in the legs when standing or walking
- Difficulty walking or maintaining balance
- Relief when bending forward or sitting
Diagnosis and Treatment:
Evaluation may include a physical exam and imaging such as X-ray, MRI, or CT scan to assess narrowing and nerve pressure. Treatment options often include medications, physical therapy, injections to reduce inflammation, and activity modification. Surgery may be considered if symptoms are severe, progressive, or limit daily function.
When to seek medical care:
Get medical care if pain persists, movement becomes difficult, weakness develops, or symptoms worsen over time. Early evaluation helps protect nerve function, improve comfort, and support safer recovery.
What Are the Symptoms of Back Injury After a Car Accident?
Back injuries from car accidents can range from mild muscle strains to serious spinal damage. Recognizing symptoms early helps prevent complications and supports timely treatment.
Common symptoms include:
- Back or neck pain: Persistent aching or sharp pain in the affected area
- Stiffness or limited movement: Difficulty bending, twisting, or turning
- Numbness or tingling: Sensations in the arms, legs, hands, or feet
- Muscle weakness: Trouble lifting, gripping, or walking
- Radiating pain: Pain that travels down the legs (sciatica) or into the arms
- Loss of balance or coordination: Trouble walking or standing steadily
- Bladder or bowel changes: Difficulty controlling function, indicating possible nerve injury
Even mild discomfort should not be ignored. Early evaluation by a spine specialist ensures proper diagnosis, prevents further injury, and helps plan effective treatment.
Protect Your Spine and Reclaim Life
Car accidents can cause back injuries, including muscle strains, whiplash, herniated discs, spinal fractures, and nerve damage. Early evaluation and treatment prevent complications and support recovery. Recognizing symptoms and consulting a skilled spine specialist reduces pain, restores mobility, and improves quality of life.
Act quickly, follow medical guidance, and commit to rehabilitation to protect your spine and return safely to daily activities. Spine health matters, don’t wait.
FAQ: Back Injuries From Car Accidents
1. How soon should I see a doctor after a car accident?
Even if pain seems mild, it’s best to get evaluated within a few days. Some injuries, like spinal fractures or nerve damage, may not show symptoms immediately. Early assessment prevents complications.
2. Can a minor accident cause serious back injuries?
Yes. Whiplash, disc herniation, and soft tissue injuries can occur even in low-speed collisions. Symptoms like stiffness, numbness, or radiating pain should be checked promptly.
3. How are back injuries diagnosed after a car accident?
Diagnosis may include a physical exam, X-rays, CT scans, or MRI. These tests help identify fractures, disc injuries, nerve compression, and soft tissue damage.
4. What treatments are available for back injuries?
Treatment depends on injury type and severity. Options include rest, medications, physical therapy, injections, bracing, and in severe cases, surgery. Early intervention improves outcomes.
5. When is surgery necessary?
Surgery may be required if there is severe pain, nerve compression, spinal instability, or persistent symptoms that do not improve with conservative care.
6. Can I return to work or daily activities after a back injury?
Many patients recover with proper treatment and rehabilitation. Activity may be limited initially, but guided physical therapy helps restore strength, mobility, and function safely.
7. How can I prevent further injury after a car accident?
Follow your doctor’s instructions, avoid heavy lifting or twisting, maintain good posture, and complete recommended rehabilitation exercises. Early care and proper recovery are key to preventing long-term issues.







